Everything you need to know about buying a TV
Our best advice for those buying a new TV

When you're looking at new TVs, there's so much jargon and marketing to sift through that it can be difficult to know what's important and what isn't. From the bare minimum basics to the advanced features you ought to know, we put together this condensed collection of buying advice and glossary of TV technology.
We have lots of detailed and technical advice on our site, digging into the specifics of various features and technologies available on today's TVs. From comparisons of specific display technologies to in-depth explanations of thee latest features, we're happy to share our expert information day after day. But when you're shopping for a new TV, you might not want a lengthy guide to every feature and option under the sun, and even our robust collection of TV reviews can't cover every model from every TV manufacturer.
- Tested and reviewed: The best TVs we've seen
- Try the best TV mounts for the TV you already own
- Latest: Amazon unveils own Omni and 4-Series Fire TVs — and they look really good
Rather than rehash what you would find in our TV buying guide or our guide to smart TVs, or any of our other more detailed articles, we've boiled down our shopping advice to key suggestions and specific terms you need to know to give you a concentrated dose of knowledge to make a great TV buying decision. It's one part vocabulary lesson, one part abridged collection of the most important takeaways from our many helpful articles.
Here's our TV shopping cheatsheet.
Resolution
Why you can trust Tom's Guide
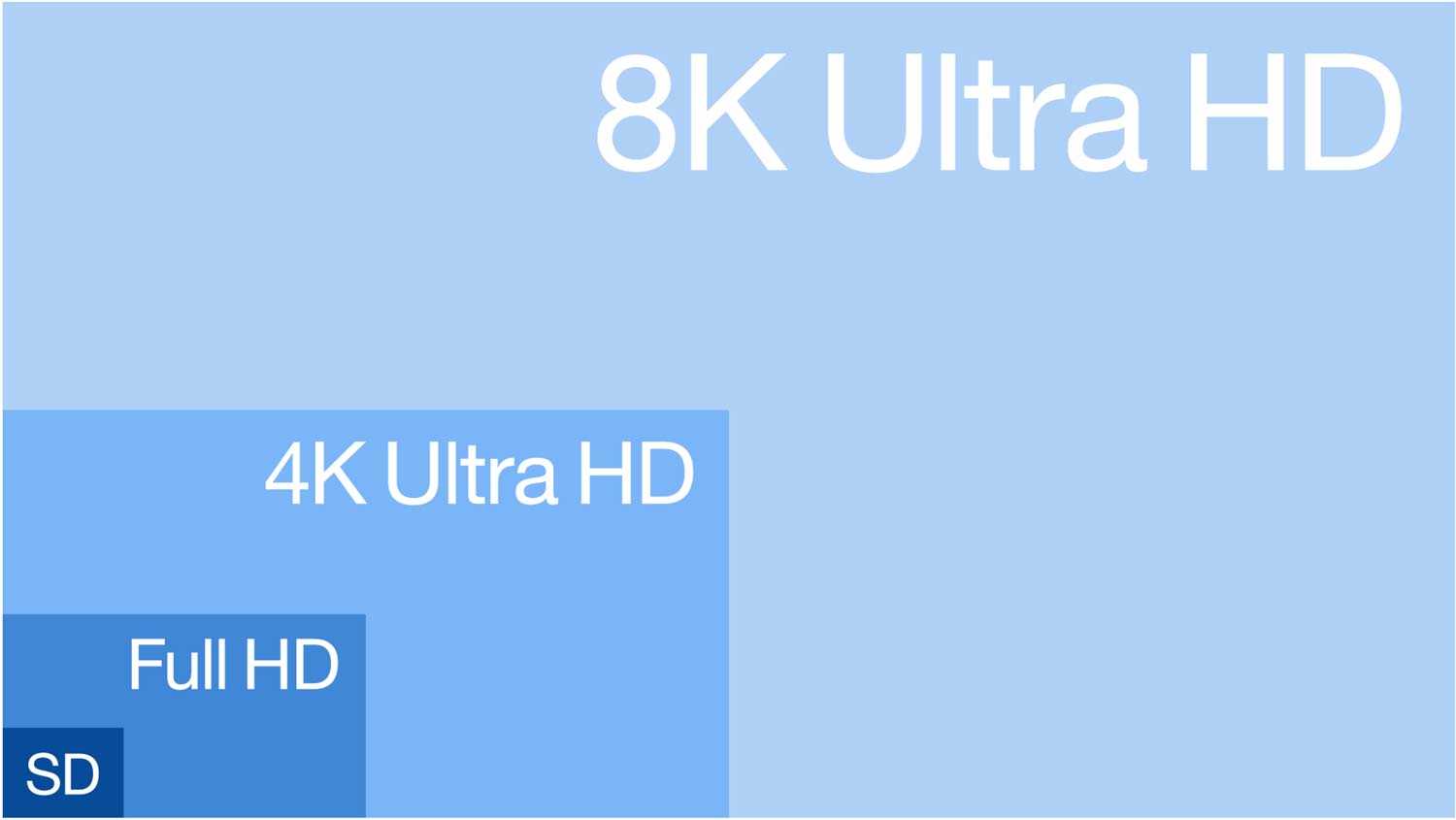
When it comes to TV shopping the most basic element is the screen, and the first big factor is resolution. With multiple resolution options on the market, these are the specifics you need to know.
720p or HD: Display resolution measuring 1280 x 720 pixels, frequently used in HDTV broadcasts, DVD media and the most common resolution used for streaming video with limited bandwidth.
1080 or Full HD: Display resolution measuring 1920 x 1080 pixels, used in modern television broadcasts, cable and satellite TV, Blu-ray media and available broadly in free and paid streaming services.
4K or Ultra HD: Display resolution measuring 3840 x 2160 pixels, commonly referred to as Ultra HD or UHD. Potentially supported by the new ATSC 3.0 broadcast standard, and available as a higher-end offering in cable and satellite, on UHD Blu-ray discs and higher-tier subscription streaming. (See the best 4K TVs we've reviewed.)
8K (also called Ultra HD): Display resolution measuring 7680 x 4320 pixels, commonly called 8K, and (confusingly) also called Ultra HD. Despite the growing number of 8K TVs on the market, there are no significant sources of 8K media. (See the best 8K TVs for recommendations and more detailed shopping advice.)
Screen size

The next significant issue is screen size. TV displays are measured diagonally from corner to corner, and the larger the TV screen, the larger the TV, and the more distance you'll need to comfortably view it. So consider the space the TV is going in before you jump at buying a larger TV.
Standard screen sizes: For most households a 55 or 65-inch TV will be plenty big, while still fitting nicely in your den or living room.
Larger screens: Bigger screen sizes of 75 and 85 inches are available, but are large enough that you'll need to think through whether you have the physical space for the TV itself, and for comfortable viewing.
Smaller screens: Smaller TVs of 50 inches or less can be a great fit in smaller apartments, dorm rooms, or as secondary TVs in the kitchen, kids bedrooms, and anywhere else you might want to put a little TV. Small TVs are also the one time you should consider anything less than 4K resolution. Anything under 43 inches is too small to properly display 4K in a way that the eye can process, making full HD resolution a good choice for smaller sets.
For more discussion of screen size, check out our guide What size TV should you buy?
If you already know what size you want your next TV to be, we've gathered our favorites in every major class of screen size:
The smallest smart TVs | Best 43-inch TVs | Best 50-inch TVs | Best 55-inch TVs | Best 65-inch TVs | Best 70-inch TVs | Best 75-inch TVs | Best 85-inch TVs
Display tech
Going beyond the basics of resolution and size, you'll want to know about display technologies. What's the difference between QLED and OLED? (Read our article QLED vs. OLED TVs: Who wins? to learn more.)
There are three primary categories to know in the TV world – LCD, QLED and OLED. While manufacturers might try to confuse the issue with different acronyms and branded names for certain technologies, it all boils down to these three options. (For now, anyway – new technologies are on the horizon.)
LCD (aka LED): The most basic form of modern TV display technology is LCD (sometimes called LED) displays, which use a liquid crystal display (LCD) panel to produce picture and color, combined with an LED backlighting to provide brightness. Some refer to these TVs as LED TVs to distinguish them from older versions that used compact fluorescent lights instead, but LED has become the basic standard now.

QLED: QLED or quantum dot displays use nanotechnology to boost color and brightness of an LCD display. Quantum dot displays use microscopic nanocrystals, which have the unique property of glowing at a particular wavelength when exposed to light or electricity. This lets manufacturers use quantum dots with LCD panels for better color and brightness. QLED TVs have gotten quite common, and it's a feature worth looking for, since they offer noticeably better picture quality than traditional LCD TVs.
Check out the best QLED TVs for our top recommendations.

OLED: The best TV technology around today is OLED, which stands for organic light emitting diode. These displays use special compounds to create ultra thin displays that can be manufactured by printing them directly onto glass. With each individual pixel capable of producing its own light, they eliminate the need for additional backlighting, making for extremely thin displays, and offering extremely high levels of contrast. If you're in the market for a premium TV, OLED is the best you'll find.
Read our guide to the best OLED TVs to learn more.
Backlight and dimming
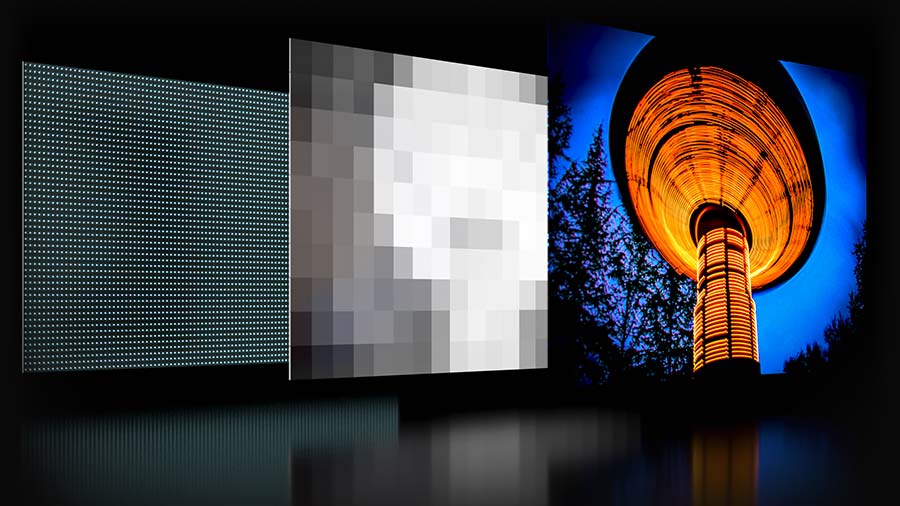

Color and contrast are only part of the display equation. In addition to panel types, You also need to look at backlighting and illumination.
What adds brightness to a TV screen is the backlight. Where the first flat screen TVs used compact fluorescent bulbs, modern-day televisions use powerful LED lights, which allow for thinner light or televisions with brighter screens.
There's several forms of LED backlighting that are offered on a TV, and some are better than others. The better options also add some expense to the TV, giving us an opportunity to spend more money.
Edge lighting: The most affordable option for TV backlight is edge lighting, which uses rows of LEDs around the edge of an LCD panel to provide brightness to the picture. The result is sometimes a little inconsistent, with notable shadowy spots and unwanted bright portions of the screen, but that may not be an issue for casual TV watching. If you want to save a buck, check out the picture on an edge-lit TV and decide whether it offers acceptable quality to you.
Dual LED: A Samsung exclusive, Dual LED backlighting upgrades edge lighting with LEDs that produce cool and warm tones of light, and will alternate those to offer slightly more dynamic lighting than traditional edge lit displays. We're not a huge fan of the technology, but Samsung offers it on some of its mid-range QLED TVs.
Direct backlight: An array of LED backlights that cover the backside of the LCD panel for brighter, more vibrant illumination. It's a great option for LCD TVs, but doesn't offer good high dynamic range.
Full array, local dimming (FALD): The best option on any LCD/LED TV is full array backlight with local dimming, sometimes shortened to FALD. This backlight setup uses a direct backlight behind the entire LCD or QLED panel, but brakes it up into several discrete zones that can be brightened or dimmed individually. This allows the TV to brighten one part of the display while darkening others, which translates into better contrast and higher dynamic range.

Mini-LED: Mini-LED TVs are relatively new, and they improve on basic FALD backlight by shrinking the LEDs down to a just a fraction of the regular size. Smaller LEDs allow for smaller, more tightly controlled backlight, with significantly more dimming zones – often offering hundreds of zones, instead of the dozen or so offered on other TVs.
Per-pixel lighting: The only option that's better than an LED backlight is when individual pixels produce their own light and can be brightened and dimmed at the pixel level. For mainstream TVs, only OLED can offer this level of lighting control, but manufacturers are working on new technologies like micro-LED and QD-OLED to challenge OLED's current supremacy.
Brand names and manufacturers
TV brands give you a sort of shorthand for a wide range of technologies and features. Here's a very high level look at the major brands you might want to consider when you're shopping for your next TV.
For more information, check out our guide to the best TV brands.
Top brands are names that you will definitely recognize – LG, Samsung and Sony. Pretty much any TV from any of these three brands will be of decent quality, and offer a good mix of performance and features at any price point.
Value brands include names like TCL, Hisense and Vizio. These brands offer better prices than the more recognizable brands, but still deliver a great 4K picture and decent smart TV functions, though you may give up a few features. These brands offer amazing deals, and are frequently featured on our best TV pages, but check out the reviews first, because there are some clunkers out there. (Check out some of our picks for the best TVs under $1,000.)
Bargain brands are the cheapest of cheap TVs. Brands like Toshiba, Westinghouse, Element, Sceptre, RCA and Polaroid – not to mention a dozen other brands you may not recognize – offer TVs priced so low that you might think they're too good to be true. They often are. (Check out the best TVs under $500 for some of our recommendations)
Smart TV tech
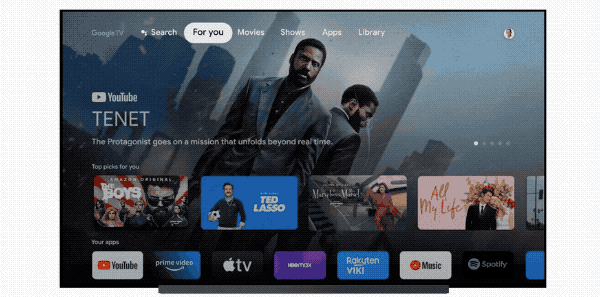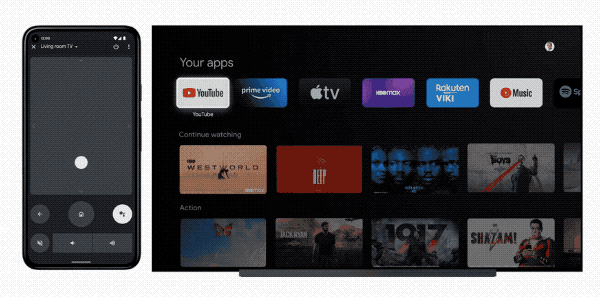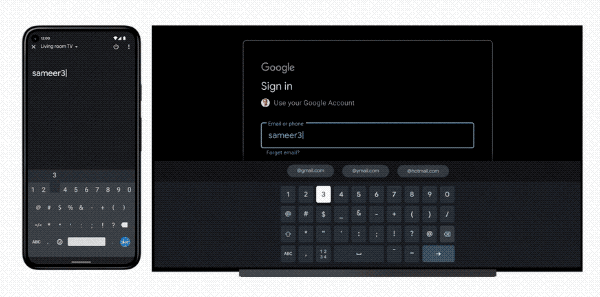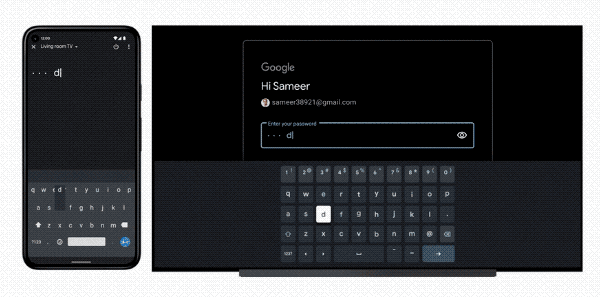
A smart TV is any set that can both connect to the internet and run apps, letting you enjoy streaming services like Netflix, Hulu and Disney Plus right on your TV without requiring a separate device. With most TVs today classified as smart TVs, it pays to know the difference between the many types of smart TV software, and why you might want to choose one over another.
Proprietary platforms: webOS, Tizen and SmartCast
The different TV makers will rely on different smart TV platforms, and each is a little different. LG uses its own webOS and Samsung uses Tizen, both proprietary software that still offer a large number of apps and features.
Samsung TVs especially rely on the broader ecosystem of Samsung products to offer an integrated experience for mobile and smart home users. If you're already living the Samsung life, a Samsung TV will enhance that experience.
Another proprietary smart TV platform is Vizio's SmartCast, which doesn't offer the same breadth of apps and features, but has improved consistently from year to year.
Third party software: Roku, Android, Google and Fire
Other brands will rely on third party software. The most popular of these is Roku TV, which can be found on a variety of TVs, from dirt cheap budget sets to premium models. We love the Roku TV platform for its wide app selection and easy-to-use interface, and it's available on some pretty high-quality TVs. (Check out the best Roku TVs for recommendations.)
Google TV and Android TV are another big name, with Google TV being the recent rebranded upgrade to Google's older Android TV platform. All told, both Google options offer perhaps the best app selection and widest number of features. Built-in Chromecast for sharing content to and from other devices is a huge plus, and Google Assistant is baked in for excellent voice interaction.
Amazon is also in the smart TV game with Fire TV, which can be found on both Amazon-made TVs and a handful of other manufacturer models sold through Amazon and Best Buy. Amazon Fire TVs offer plenty of apps and features, including built-in Alexa voice assistant, but they tend to be on the cheaper end, and Amazon TVs can be a little heavy on the advertising.
High dynamic range (HDR)

One of the biggest features to come to TVs in recent years is high dynamic range, or HDR. Thanks to technologies like LED dimming zones and OLED's pixel-level brightness control, modern TVs can adjust the brightness of different parts of the screen, allowing it to display brighter brights and deeper darks for a much more realistic and immersive picture. It also translates into more vibrant color, which makes everything look better.
Doing this requires media to include extra information about the brightness and color of each scene, above and beyond what normal video signal includes. Called metadata, this extra data comes in a few different formats, and they differ a little according to which format or standard is being used. Here's a quick rundown of the main HDR formats, and the technologies that enable them.
Learn more about it in our article What is HDR TV, and why does it matter?
HDR 10 and HLG: HDR10 is the industry standard for high dynamic range content, and will work with any HDR content. Alongside it is HLG, which stands for hybrid log gamma, and allows HDR-like brightness control for live broadcast content. Any HDR-capable TV will be able to work with these basic standards.
Learn more about HLG in our article What is HLG HDR?
Dolby Vision and Dolby Vision IQ: The proprietary format Dolby Vision offers more specific instructions than basic HDR10, allowing for more flexibility and variety in how brightness and color are handled from scene to scene.
The resulting picture should deliver an even better HDR experience, but it will vary depending on the TV – mediocre performance can blunt the effectiveness of even the best HDR content.
And there's one more twist. Dolby Vision IQ is a variation on the format that uses ambient light sensors to determine the lighting levels in the room where the TV sits, and will adjust HDR levels to provide an optimized version of the content. The feature tends to be more expensive, showing up only on more premium smart TVs. In our experience, Dolby Vision is great, but Dolby Vision IQ is more of a "nice to have" option.
Learn more in our article What is Dolby Vision? (And how to get it).
HDR10 Plus: Samsung has its own competitor to Dolby Vision, called HDR 10 Plus. While the 10 Plus format isn't as broadly supported in media and streaming as Dolby Vision, it does have the distinction of being supported by Samsung TVs – Dolby Vision is not.
Ports and connectivity
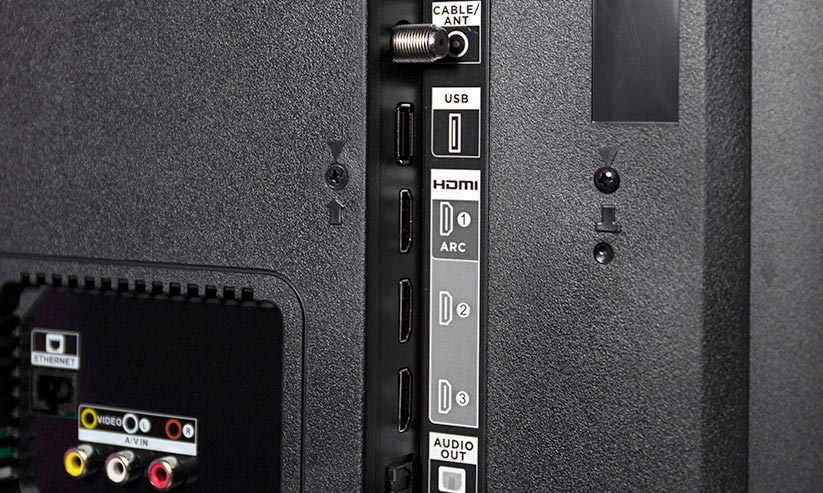

Look on the back of any TV and you'll find a handful of ports and connectors, along with labels that may or may not make any sense to you. Here's a quick rundown of the ports that are most important, and what to look for to get a better deal.
HDMI: The standard for video and audio connectivity across TVs, media players and audio products, HDMI is a simple all-in-one solution for what used to require lots of separate cables. But it's not entirely straightforward, as new HDMI standards have added new features and functions to seemingly identical HDMI ports.
- HDMI 1.4 - Supports 1080p and 720p video and sound, but generally isn't used on modern 4K TVs.
- HDMI 2.0 - Supports 4K picture and refresh rates up to 60Hz. Unless specifically identified as HDMI 2.1, this is the most common HMDI version in use on today's TVs.
- HDMI 2.1 - used by the latest game consoles and found on higher-end TVs, HDMI 2.1 offers more bandwidth for supporting higher frame rates, up to 8K resolution, and a number of distinct features.
Find out more about the latest HDMI offerings in our article What is HDMI 2.1? Here’s everything you need to know.
ARC: Built into the HDMI standards presently used is a feature called Audio Return Channel, or ARC. It lets you use a single HDMI cable to connect a TV and soundbar, offering two-way communication between devices over a single HDMI connection. Essentially, the HDMI ARC port lets you use HDMI as both an input and an audio output.
A newer version of ARC, called enhanced audio return channel (eARC). The biggest improvement eARC offers is support for full-resolution audio signal, meaning that it supports Dolby Atmos and other uncompressed sound formats.
Read our guide What is HDMI ARC? to learn more.
USB: Today's smart TVs will also include at least one USB port. These ports can be used for connecting a flash drive for viewing media on the TV, or to power devices over USB, such as a streaming stick or amplified antenna. We recommend opting for more ports when you can.
Ethernet and Wi-Fi: With today's smart TVs requiring internet connectivity for so many features, TVs come with built in connectivity. All support Wi-Fi, but Ethernet is the better option – it may not have the convenience of wireless, but an Ethernet cable will offer a faster, more stable connection. Most TVs offer both options, but some budget models save a buck by going Wi-Fi only.
Bluetooth: Whether you want to wirelessly connect a set of surround sound speakers for room-filling audio, or a pair of wireless headphones for discreet listening that won't wake your family at night, Bluetooth can make it happen. Most TVs are equipped with Bluetooth these days, but check the specifications for any TV you're considering, as some TVs use Bluetooth exclusively for pairing the remote control, or will let you connect audio devices, but not peripherals like a keyboard.
Gaming features
If you enjoy console gaming of any type, you'll want to know the key features that make a good gaming TV. With modern game consoles offering advanced features and higher resolution and frame rates, you want to make sure your TV has the feature support it needs.
Check out our guide to the best 4K gaming TVs for all of our current recommendations and more detailed shopping advice.
Connectivity: HDMI 2.0 is fine for most 4K gaming, but if you want to game in 4K at higher frame rates or take advantage of features like variable refresh rates or automatic low-latency modes, you'll need a TV that supports HDMI 2.1. (See our discussion of HDMI above.)
Refresh rate: The higher a TV's refresh rate, the better it will be able to handle fast motion, especially for gaming. Most 4K TVs are capped at 60Hz, but more premium sets can handle up to 120Hz, which matches the performance of newer consoles like the PS5 and Xbox Series X.
Lag time: The interval between an image or button press registering on the console and the resulting change displaying on screen. Measured in milliseconds, we recommend gamers look for TVs with a lag time of 20ms or less.
Refresh rate
The refresh rate describes how many times per second a picture is refreshed on the screen. Expressed in Hertz (Hz) it translates to what frame rate the TV can handle, with a 60Hz display capable of displaying 60 frames per second. Higher refresh rates become more important when dealing with fast-paced content, such as live sports and gaming.
One thing to note is that TV manufacturers will often quote an "effective" refresh rate. These numbers are always higher than the actual panel refresh rate, and reflect the use of techniques like backlight flicker and video processing, and don't describe the actual refresh rate of the display panel.
30Hz: The refresh rate used by older HDMI standards and media, including some 4K-capable game consoles. Most movies and shows are in this range, but the majority of TVs sold now can handle higher refresh rates.
60Hz: The most common refresh rate for older 4K TVs. Most gaming consoles top out at 60 frames per second, but newer consoles can go higher. For TV shoppers, 60Hz is what we recommend as the minimum acceptable refresh rate, even on budget models.
120Hz: The most common refresh rate on current 4K TVs, 120Hz exceeds the needs of most media. Gamers will get the most out of this higher refresh rate, which requires a newer console and HDMI 2.1 connectivity.
240Hz: Some TVs will tout an effective refresh rate of 240Hz, but the actual rate, as a rule, is really 120Hz.
High-Frame Rate (HFR): High Frame Rate support refers to anything over 30 frames per second, whether it's movies, sports broadcasts or gaming. Higher frame rates offer smoother motion, and usually are paired with better video processing for a clearer image.
Variable Refresh Rate (VRR): A new gaming feature offered in the HDMI 2.1 spec that lets a TV and game console synchronize the output frame rate with the panel refresh rate to eliminate judder and tearing for smoother gameplay.
Learn more in our articles about the best refresh rates for TVs, and A gamer's guide to refresh rates and response times.
Contrast
Contrast describes the difference between the brightest and darkest shades that the display can produce. This is expressed as a numeric ratio, such as 2,000:1. TV manufacturers place a lot of emphasis on contrast numbers, but luckily, this is one area where you don't need to worry that much.
In general, the contrast numbers quoted by manufacturers and retailers mean very little. Contrast numbers are highly inflated, and measurement standards are so varied that the numbers wouldn't mean much anyway.
What does matter is how the set actually looks, and this is where actual contrast – not the quoted contrast rating – comes into play. This can be adjusted in the TV settings under "brightness" and "contrast" settings.
Audio
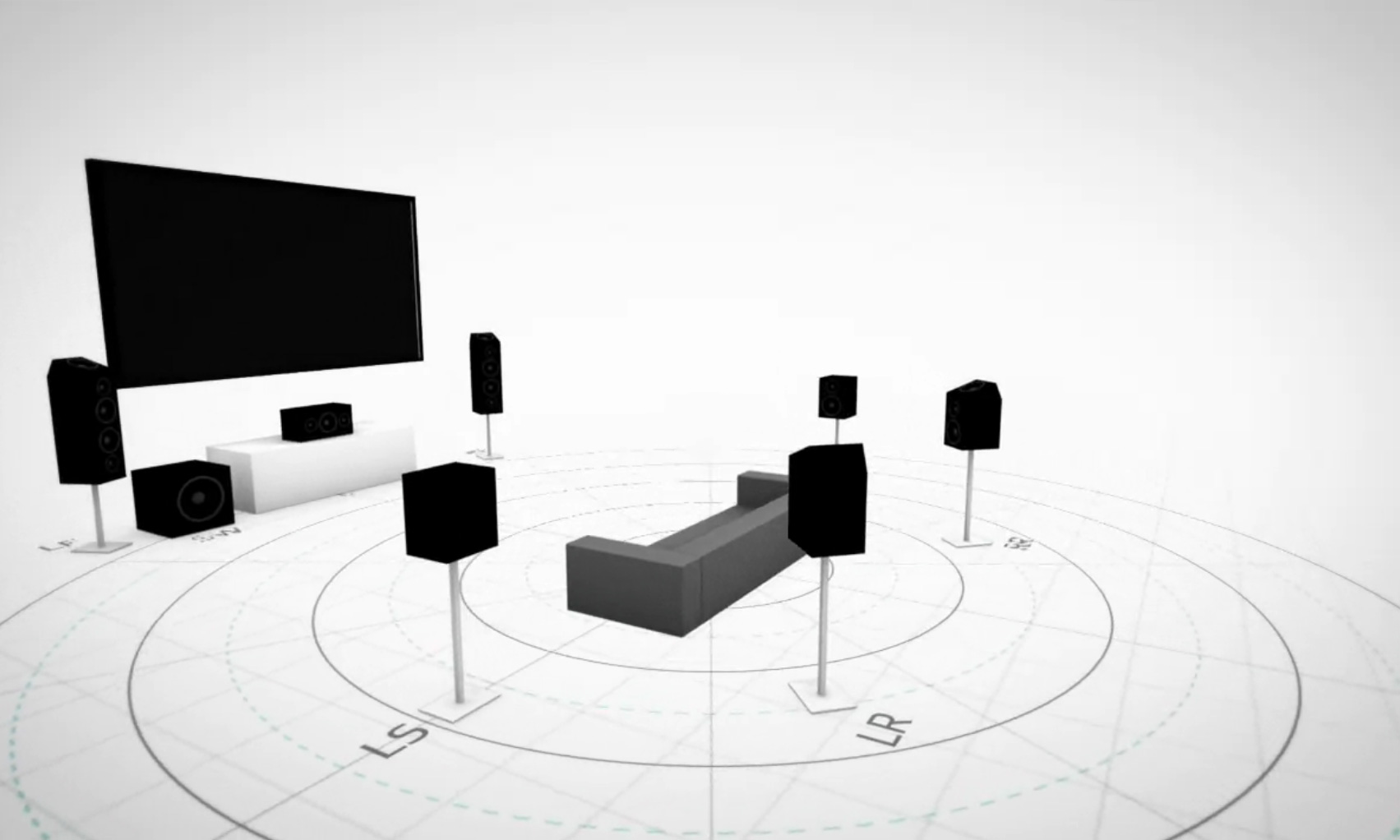
There's more to TVs than just the visual, and audio is an important piece of what makes a great TV. From clear dialogue to booming sound effects and floor rumbling bass, audio quality is half the movie or show.
The problem is that TV audio is a challenge. Fitting big, room-filling sound inside the increasingly thin chassis of most modern TVs is a feat that requires a lot of engineering and carefully tuned audio, and that means that better audio is expensive. Most TV manufacturers settle for good-enough audio on all but their most premium TVs.
In general, we recommend pairing a TV with a soundbar to skip the audio issue entirely. That said, there are a few specifics you should keep an eye out for.
Soundbar: A separate device that combines center, right and left channel audio (and sometimes additional channels) into a single unit that sits below a TV. The design and size of a soundbar allows it to produce big, better sound than most TVs can match, and they can be paired with a subwoofer or additional speakers to create a full surround sound system.
Check out the best soundbars we've reviewed for our recommendations and shopping advice.
Multi-channel sound: There are several options for multichannel sound, but the basics are all the same – instead of pumping all of a TV's sound out of two stereo speakers, multichannel audio uses multiple speakers, adjusted for specific speaker positions, to create a rich and immersive sound experience.
With formats from Dolby Digital and DTS, multichannel sound is also expressed as a series of numbers, such as the standard 5.1 (five speakers, one subwoofer) or 7.1 (seven speakers, one subwoofer), 5.1.2 (the standard 5.1 system with an additional two up-firing speakers for vertical sound), and up to 9.1.2 and higher.
Dolby Atmos: Dolby Atmos is a proprietary audio format that combines surround sound multichannel sound with height channels, specifically used with ceiling-mounted speakers or up-firing speakers that reflect sound off of the ceiling, to offer more vertical and immersive sound. Several TVs offer Dolby Atmos support for an Atmos-enabled soundbar or speaker system, and a very few offer Atmos in the TV itself, with upfiring speakers built in.
Learn more in our article Dolby Atmos explained: What it is, how it works and where to get it.
Price
Last, but far from least, is price. Good 4K TVs can be had at all different price levels, but you can generally expect a few differences depending on how much you pay.
Premium TVs: Generally priced at $1,000 or more, with the best TVs exceeding $2,000. These are the best of the best, with excellent picture quality, sound that may not require adding a soundbar, and smart TV functions that do everything from asking Alexa or Google Home for movie recommendations to checking your doorbell camera or letting you jump on a video call with friends and family.
Several of the top models on our list of the best TVs fall into this price range, simply because the best features and performance are reserved for more expensive models.
Mid-range TVs: Priced between $500 and $1,000, you can find a great 4K smart TV for under a grand, but that may require giving up some of the nicer features. You can find these TVs with features like 120Hz panels, Dolby Vision HDR and lots of HDMI ports, but you may not find all of those things in the same TV. You also won't find larger screen sizes, top display technologies like OLED or higher 8K resolution displays.
Check out the best TVs under $1,000 for our favorites in this price range.
Budget-friendly TVs: Priced at $500 or less, you can get a decent sized 4K TV and features, but you'll have to hunt for the right combination of what you want and the price you're after. Getting a better TV at these lower prices will often mean settling for a smaller screen size, skipping advanced video processing, and giving up on the more advanced smart features. And sound quality isn't great in this price range, so you'll definitely want to pair your TV with a soundbar.
Check out the best TVs under $500 for our budget-friendly recommendations, which includes picks for the best TV under $400 and under $300.
Ready to narrow down your search? Check out the best TVs by brand, price range or screen size, check out our picks for the top models in each.
Best TVs | Best 4K TVs | Best smart TVs for streaming | Best TVs for gaming
The best TVs under $1000 | The best TVs under $500
Best TV brands | Best Samsung TVs | Best TCL TVs | Best LG TVs | Best Roku TVs | Best OLED TVs | Best QLED TVs | Best 8K TVs
The smallest smart TVs | Best 43-inch TVs | Best 50-inch TVs | Best 55-inch TVs | Best 65-inch TVs | Best 70-inch TVs | Best 75-inch TVs | Best 85-inch TVs
And don't forget to watch out for the latest TV reviews.
Sign up to get the BEST of Tom's Guide direct to your inbox.
Get instant access to breaking news, the hottest reviews, great deals and helpful tips.
Brian Westover is currently Lead Analyst, PCs and Hardware at PCMag. Until recently, however, he was Senior Editor at Tom's Guide, where he led the site's TV coverage for several years, reviewing scores of sets and writing about everything from 8K to HDR to HDMI 2.1. He also put his computing knowledge to good use by reviewing many PCs and Mac devices, and also led our router and home networking coverage. Prior to joining Tom's Guide, he wrote for TopTenReviews and PCMag.

