TV ports explained: What all those HDMI, USB and other connections are for?
Learn the ins and outs of your TV's inputs and outputs

If you're not someone who sets up a new TV every week the way I am, then you're probably not very familiar with the different connections and ports found on today's smart TVs. And, if you're like most people, the only time you really look at those connections is when you're trying to set up a new TV or add a new device, like a game console or Blu-ray player. Which can make those occasional excursions behind the TV a little intimidating. There's a lot of connectors, and you may not be sure what most of them do.
We are here to help. This handy guide will identify the most common ports found on modern smart TVs, and help you know what specific details are important for getting the right connection for the right device.
- The best TVs we've tested and reviewed
- Need help? How to set up your new smart TV
- Plus: How to watch the Halloween movies in order online
Where do I find the ports on my TV?
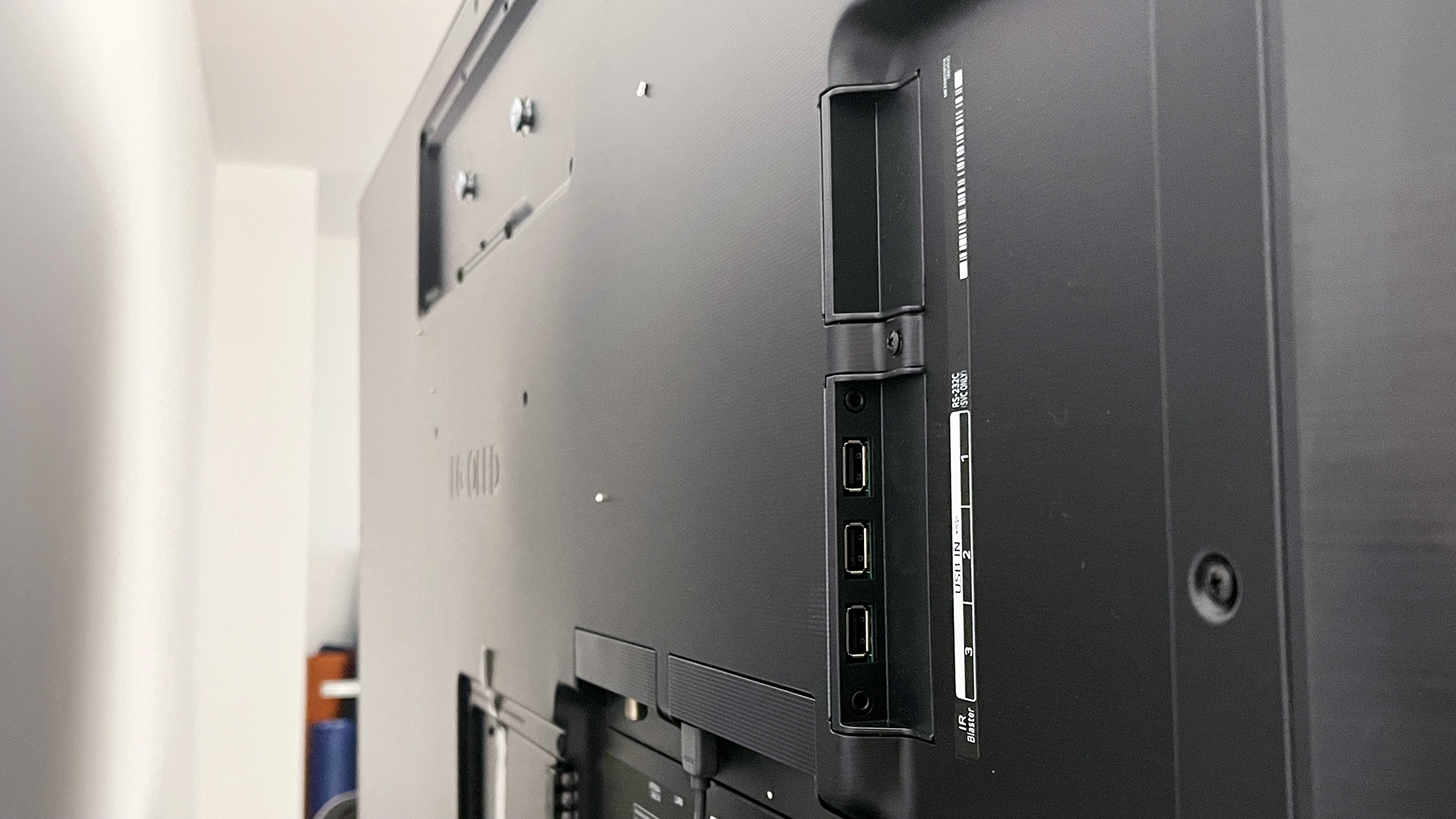
On the majority of smart TVs, you will find the ports on the back of the set, usually near the right or left side of the chassis for easy access. While many TVs consolidate all of the ports into a single panel of connections, some sets have two — one for the primary HDMI and USB connections, and a second for less-used ports, like Composite video and Ethernet.
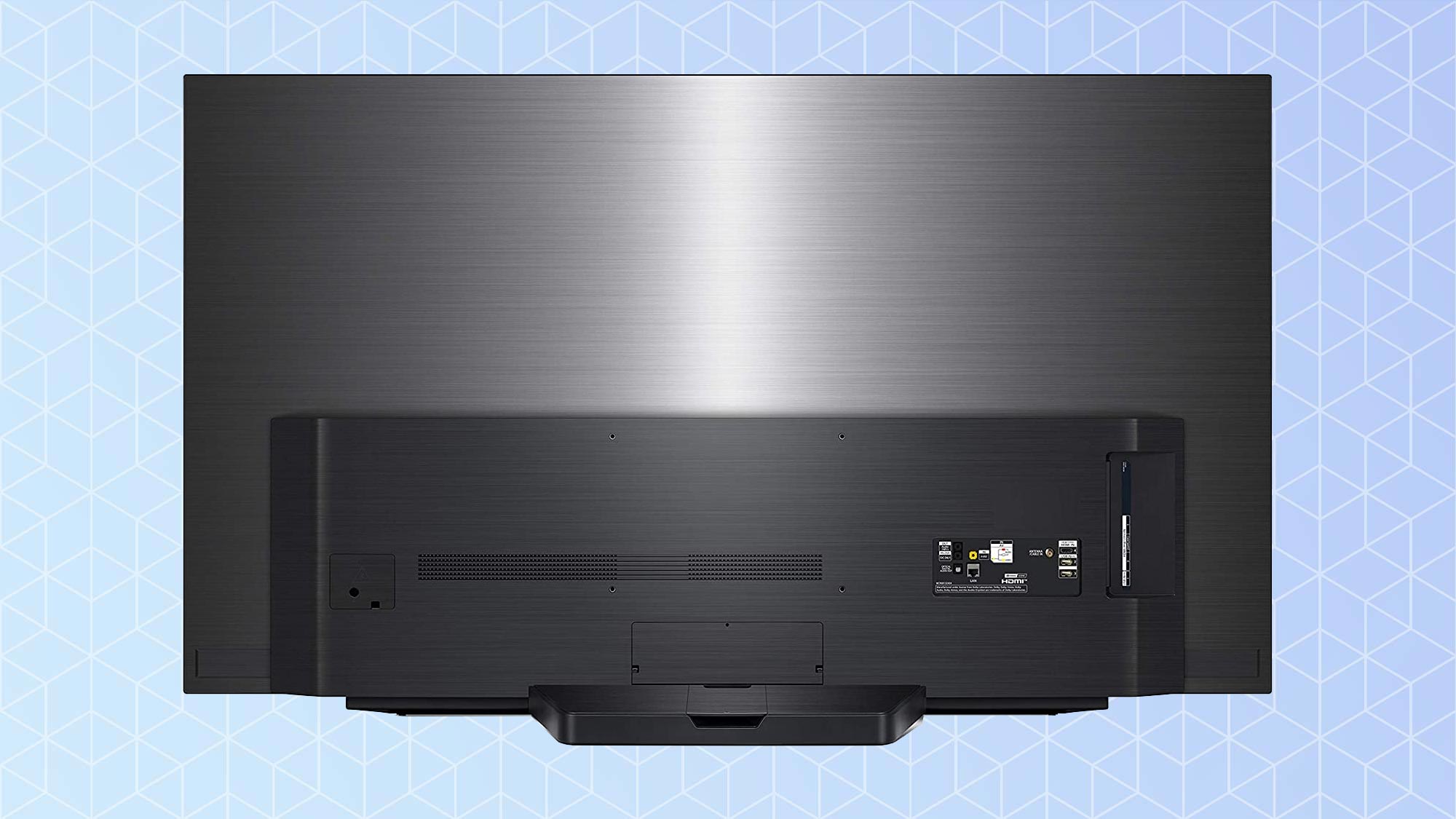

In some instances, a TV will have a separate box that includes all of the usual TV ports, connected to the TV by a single cable. This is the case with Samsung's OneConnect box, found on several of it's high-end TVs, as well as select OLED models from LG.
Video and audio connections
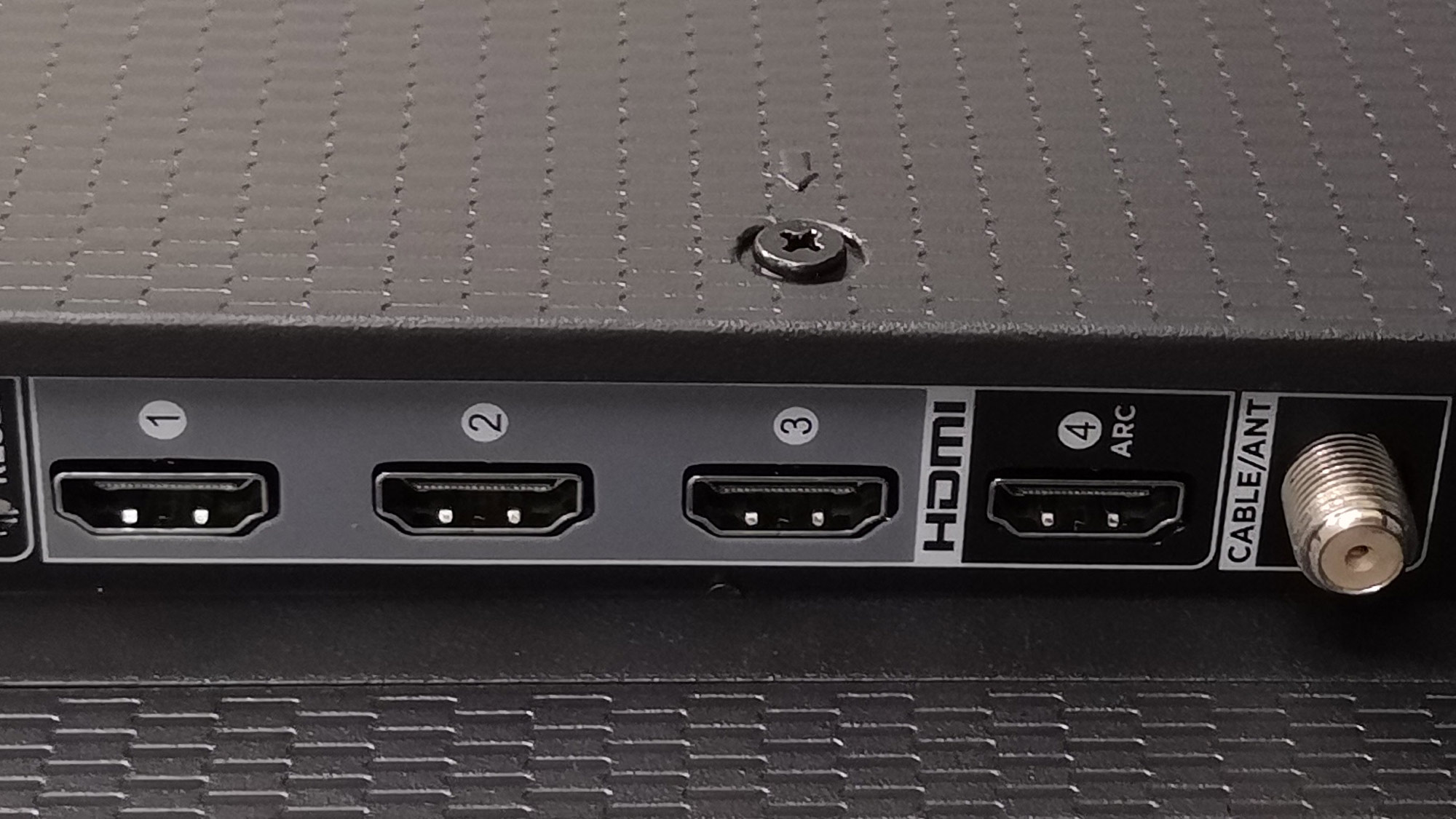

HDMI: HDMI stands for High-Definition Multimedia Interface, and is the standard connection for modern video and audio across TVs, media players and audio products. Almost any device you want to connect to your TV will use HDMI, but that doesn't mean that the standardized HDMI connector will always offer the same connection and features. With a standardized connector shape and digital signal that can carry everything from ultra HD video and surround sound to internet data, HDMI is a versatile connection. But there's more than one version of HDMI, and new HDMI standards have added new features and functions to seemingly identical HDMI ports.

In fact there are three primary versions of HDMI that you're likely to find on today's TVs, each with slightly different capabilities and features. If you're lucky, these are clearly marked on your TV, along with identifying what standard they use. More often however, you'll need to dig into the user's manual or find the product page for your TV and look at the technical specifications to determine which are which.
- HDMI 1.4 - Supports 1080p and 720p video and sound, but generally isn't used on modern 4K TVs.
- HDMI 2.0 - Supports 4K picture and refresh rates up to 60Hz. Unless specifically identified as HDMI 2.1, this is the most common HMDI version in use on today's TVs.
- HDMI 2.0a - An update to HDMI 2.0 that added support for High Dynamic Range (HDR) metadata.
- HDMI 2.0b - An update to HDMI 2.0 that added support for Hybrid Log Gamma (HLG) video, which is a different form of HDR used in TV broadcasting.
- HDMI 2.1 - used by the latest game consoles and found on higher-end TVs, HDMI 2.1 offers more bandwidth for supporting higher frame rates, up to 8K resolution, and a number of distinct features. Here are the best TVs with HDMI 2.1.
Generally speaking, most current TVs have 3 or 4 HDMI ports (we recommend opting for more when you can). If you find yourself with more devices than you have ports, you should probably get one of the best cheap HDMI switchers to add some extra connections.
Sign up to get the BEST of Tom's Guide direct to your inbox.
Get instant access to breaking news, the hottest reviews, great deals and helpful tips.
Find out more about the latest HDMI offerings in our article What is HDMI 2.1? Here’s everything you need to know.
ARC or eARC: It's also likely that one of those HDMI ports will be labelled ARC, which is short for Audio Return Channel, a feature of some HDMI connections. It offers two-way communication between devices over a single HDMI connection, letting you use a single HDMI cable to connect a TV and soundbar, using that single HDMI as both an input and an audio output.
A newer version of ARC is included in HDMI 2.0 and 2.1, called enhanced audio return channel (eARC). The biggest improvement eARC offers is support for full-resolution audio signal, meaning that it supports Dolby Atmos and other uncompressed sound formats.
Learn more in our guide What is HDMI ARC?
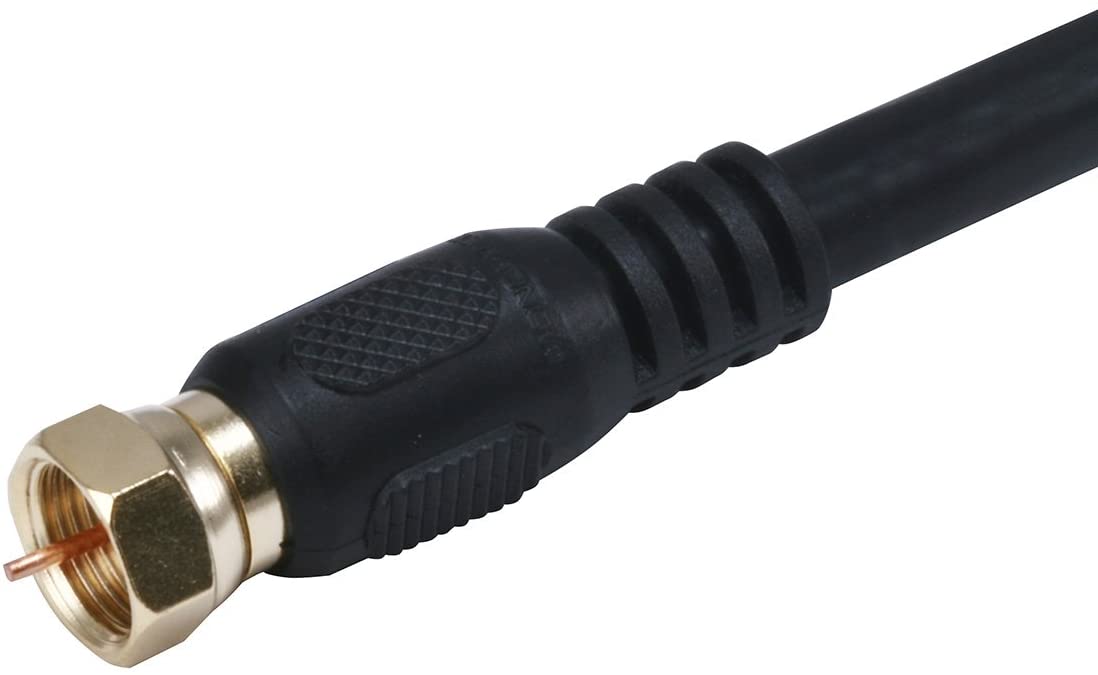

Coaxial/RF connector: A threaded connection used with coaxial cable for connecting a TV antenna or older cable and satellite TV equipment (though cable and satellite now use HDMI exclusively). This connection uses a screw-on RG-6 or RG-59 cable, and feeds into the TV's built-in TV tuner. Because coaxial cable is used to transmit both UHF and VHF radio waves, this is the standard connection for over-the-air TV signal, including current ATSC 1.0 and ATSC 3.0 digital standards.
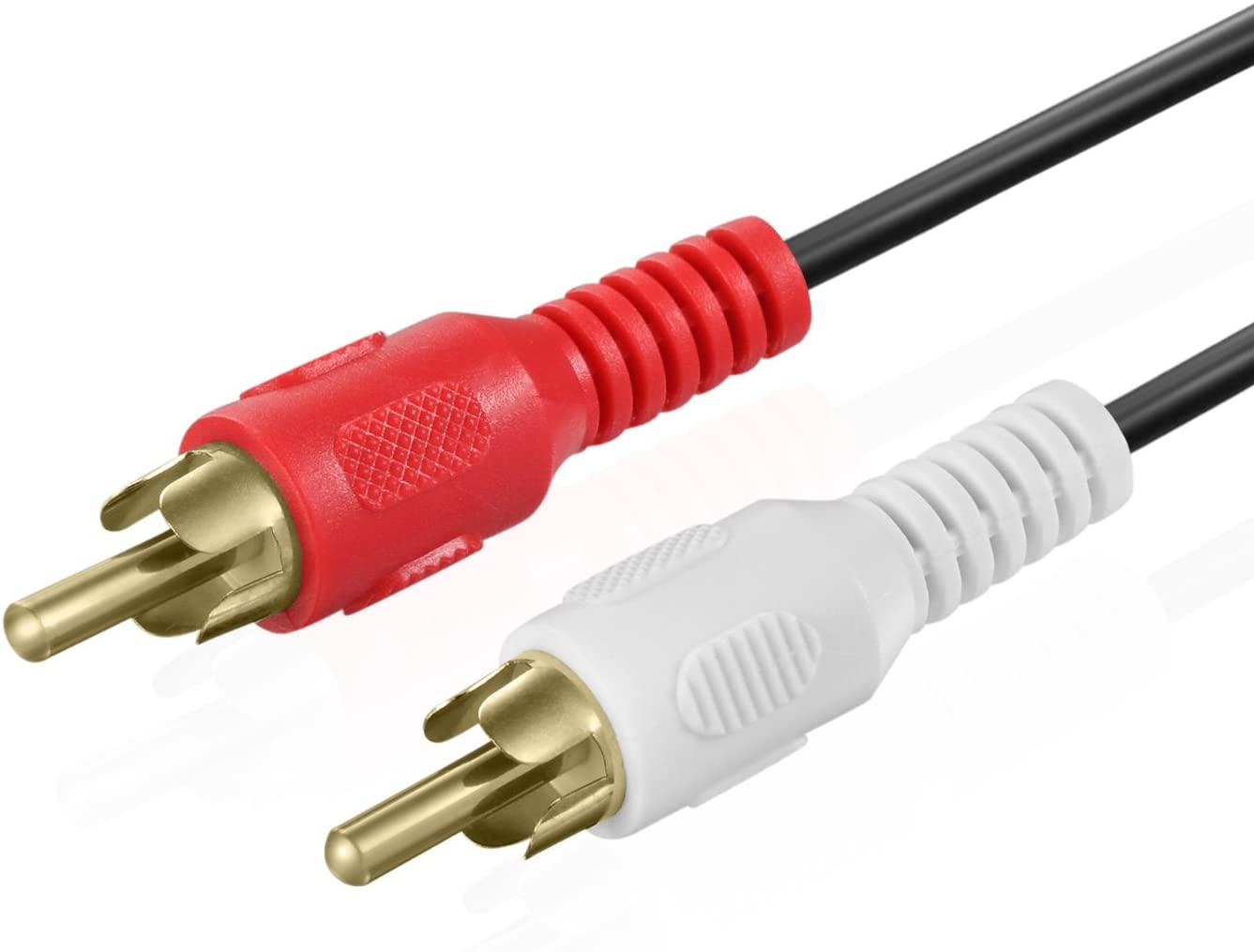
RCA connection: This round style of plug is often referred to as an RCA connection, which is short for Radio Corporation of America, the company that developed the plug design. RCA plugs are used for audio, composite video and component video connections.
Composite video: An older video connection that's still found on current smart TVs, and can be identified by a yellow RCA connection, or sometimes a yellow headphone jack-style connector (generally with an included headphone jack-to-RCA adapter). This older standard uses analog video signal, and doesn't support HD video formats, but is useful for connecting older devices, like DVD players and retro gaming equipment.
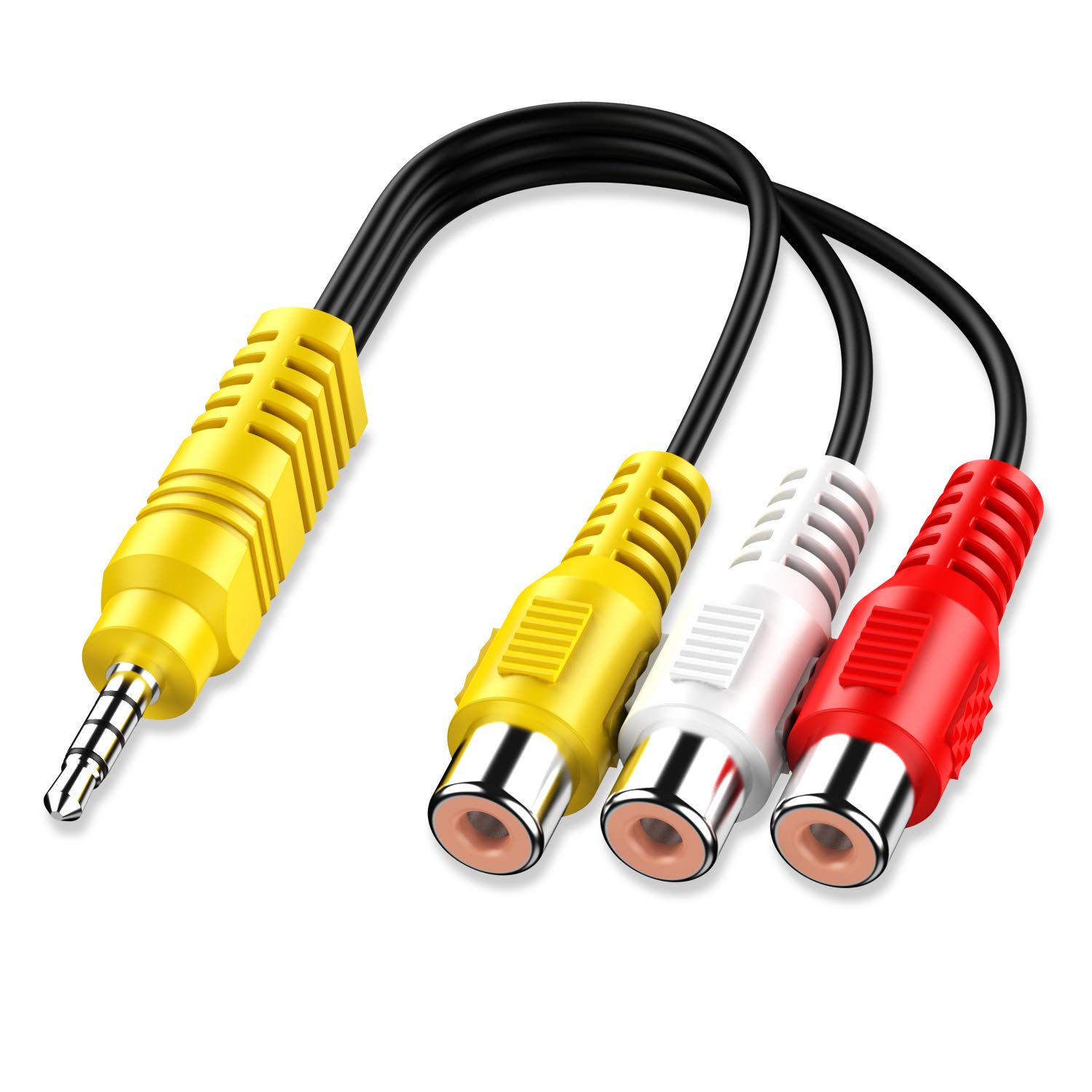

Often on modern TVs, this connection will look very different, using a headphone jack-style connection that is marked yellow or labeled "AV input." This requires an adapter, which combines composite video with RCA stereo sound on a single connection.
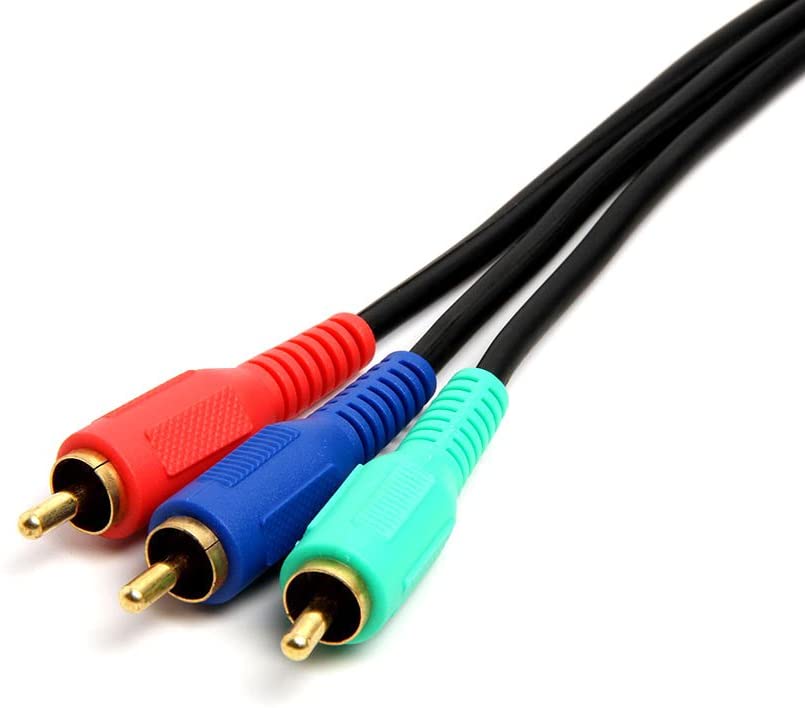

Component video: Another older video connection (and one which has largely disappeared from current TVs), is component video. While it uses the same RCA type connectors as composite video, it carries analog video signal that has been split into three separate signals for higher picture fidelity.
Stereo analog audio: Easily identified by a pair of red and white inputs, this audio connection is used for stereo sound, with the white connection carrying the left channel signal and the red connection carrying the right channel.
Headphone/3.5-millimeter audio jack: A familiar sight that might still leave you confused is a normal looking headphone jack. Though rarely located in a convenient spot for your average set of wired headphones, you can, in fact, use this jack for private listening with a longer audio cable. The connection is also used for connecting wired stereo speakers.

Digital optical audio: (Sometimes labelled TOSLINK or S/PDIF.) An audio connection originally developed by Toshiba, which uses fiber optic cable and pulsed light to send digital audio signals. Though it was a cutting edge technology in it's day – digital optical audio was once the must-have connection for multi-channel sound – it doesn't offer the same broad format support of HDMI, and is limited to a maximum 16-foot cable length. This older audio connection is still found on many TVs thanks to the prevalence of older audio hardware.
Data connections
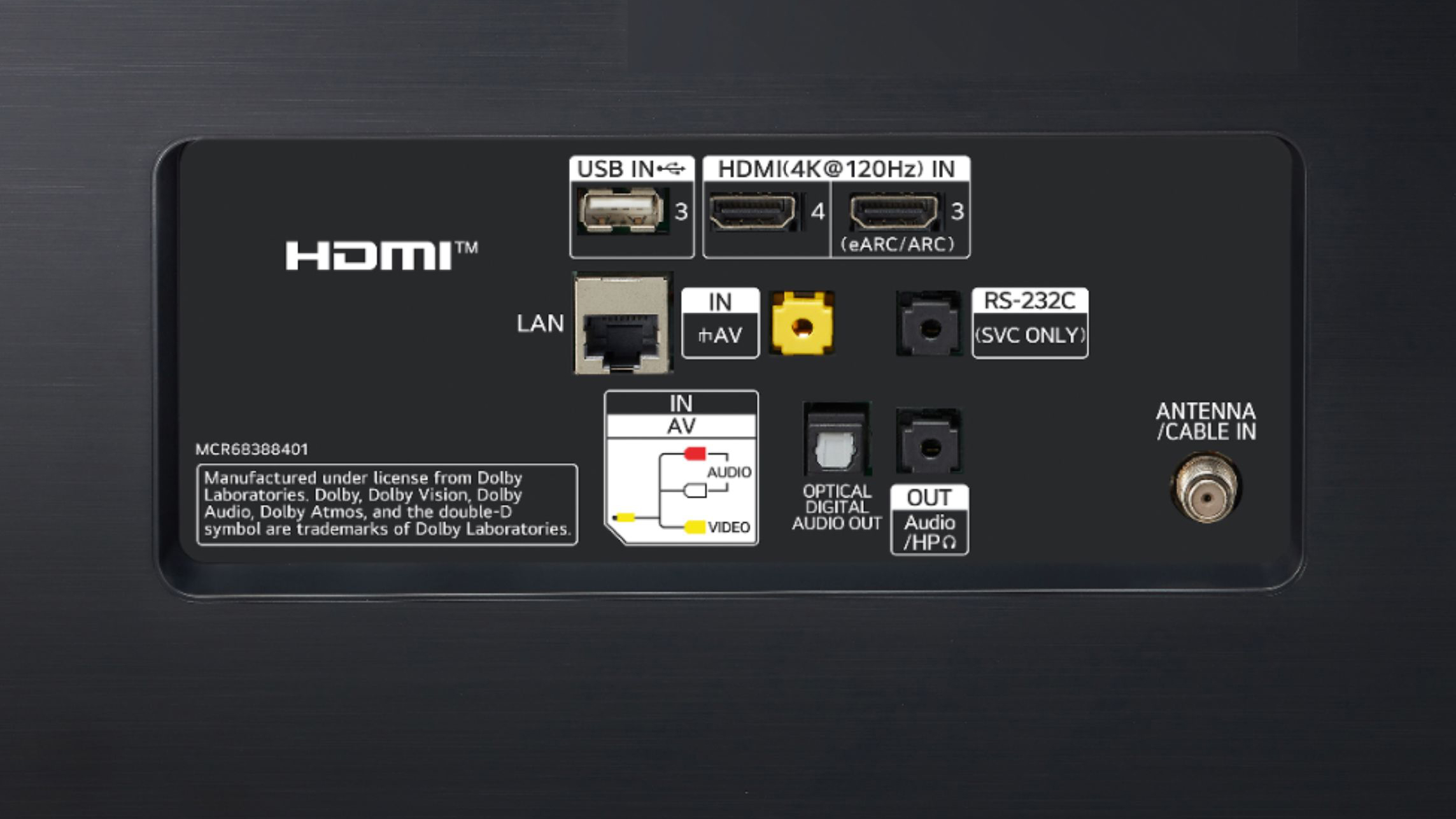
USB: A common connector on everything from smart TVs to laptops is USB. These ports can be used for connecting a flash drive for viewing media on the TV, or to power devices over USB, such as a streaming stick or amplified antenna.
But the USB port on your smart TV is a little different than the one you might use on your MacBook Pro. For starters, it uses a USB A connector, which was once ubiquitous for all USB connectivity, but is being supplanted by the more compact USB type-c connector. Additionally, the majority of USB ports on TVs use USB 2.0, an older standard that offers enough bandwidth for things like sharing photos and video, but not enough for more intensive data transfers.

Ethernet: Ethernet or Local Area Network (LAN) is a wired connection to your home network. While most people will opt for Wi-Fi to connect their smart TV for streaming and other online uses, Ethernet will actually offer a higher data transfer rate, and is free from the interference that Wi-Fi can sometimes experience in crowded environments with lots of wireless devices. If possible, we recommend connecting smart TVs over Ethernet.
Wi-Fi: One of two important connections that you won't see on the connector panel of your smart TV is Wi-Fi. The majority of current TVs use 802.11 AC Wi-Fi, which is a common, but aging standard. It's sufficient for streaming full HD and even 4K video, but it's prone to becoming a bottleneck in certain situations.
Some newer TVs, such as Samsung's latest 8K TVs, are equipped with the newer Wi-Fi 6 standard or the supercharged variant Wi-Fi 6E. These newer standards offer more data throughput for handling the increased demand of 8K video, but do require a compatible router with the same faster standard.
Bluetooth: The other connector without a port is Bluetooth. Used for both wireless audio and data transfer, Bluetooth can be used for a variety of devices, from wireless headphones and speakers to peripherals more common to the office, such as keyboards and game controllers.
Most TVs are equipped with Bluetooth these days, but check the specifications for any TV you're considering, as some TVs use Bluetooth exclusively for pairing the remote control, or will let you connect audio devices, but not peripherals like a keyboard.
Less common connections
If you're at all familiar with TV ports, or even have just taken a moment to familiarize yourself with the basic connections listed above, you might still find that some TVs have a connection or two that aren't found on that list. These unusual connectors generally aren't used by the end user, because they're not for connecting any sort of media device or entertainment equipment.
Instead these specialized ports are for more specialized uses, like adding functionality for custom installations, or providing technician access for calibration.
One irregular port you might find is an RS-232 connection, which can take a couple of different forms. It may look like a serial port (which it effectively is) or it can look like a headphone jack. This connection is used by technicians to run diagnostics and system updates on smart TVs.
Another might be labelled IR Blaster. It uses a headphone-style connector, but isn't an output for sound, but an input for an IR sensor, letting a new sensor for the remote control to be placed in a convenient spot when custom installations block the built-in sensor or make it difficult to use.
- Best TVs with Chromecast built you can buy right now
- What's the difference? Google TV vs. Android TV
Brian Westover is currently Lead Analyst, PCs and Hardware at PCMag. Until recently, however, he was Senior Editor at Tom's Guide, where he led the site's TV coverage for several years, reviewing scores of sets and writing about everything from 8K to HDR to HDMI 2.1. He also put his computing knowledge to good use by reviewing many PCs and Mac devices, and also led our router and home networking coverage. Prior to joining Tom's Guide, he wrote for TopTenReviews and PCMag.

